VEGAFLEX: Measurement of level and interface with guided wave radar (GWR)
What terms are used in connection with "Guided Radar?"
There are several terms for the "Guided Radar" measuring method, all of which have the same meaning:
- Signal runtime measurement
- Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR), TDR sensors, TDR measurement
- Guided microwave
- Guided Wave Radar (GWR), GWR transmitter, GWR measurement
How does level measurement with guided wave radar (GWR) sensors work?
Whether a GWR transmitter is measuring liquids or solids, a concentrated radar pulse travels from the sensor down the metallic probe (rod, cable or coaxial probe), contacts the product and returns to the sensor.
Guided wave radar technology is similar to through-air radar in terms of setup and operation. GWR devices are typically installed at the top of a tank with a probe (often called a waveguide) extending inside the tank and contacting the product inside. The sensor sends a concentrated radar pulse down the probe and that pulse hits the product and reflects back up the probe to the sensor. Electronics integrated into the sensor then use the pulse’s travel time to calculate distance. That distance correlates to a level measurement.
A guided wave sensor is one example of time-domain reflectometry (TDR). A TDR sensor measures reflections along a conductor – in this case, the probe conducting the radar pulse.
What are the advantages of guided wave radar?
Guided wave radar technology is ideal for a variety of applications because it is unaffected by fluctuations in
- pressure
- temperature
- or density
Setup is simple and safe, making commissioning and retrofitting virtually effortless. In addition to level, guided radar sensors can measure the interfaces of liquid separation layers. This is called interface measurement.
One major benefit of guided wave radar instruments is their excellent performance in applications where foam is present. The highly-concentrated radar pulse gives a very precise continuous reading through foam. Other level measurement technologies perform inconsistently or fail altogether in such difficult applications. Guided wave radar sensors are also the best means of level measurement in a stilling tube or bypass system.
💡 Radar vs. Guided Radar (TDR) – What are the differences between the two measuring methods?
We need your consentThis content is provided by an external provider. If you activate the content, personal data may be processed and cookies set.What are common applications for GWR level transmitters?
Guided wave radar is extremely versatile and can be found in almost every industrial sector. Whether in bitumen or liquefied gas, in storage containers or standpipes, in a metering tank or in tank farms, guided wave radar measures the level or interface (separation layers) of liquids with great reliability and accuracy. The focused microwave energy TDR sensors emit allows for accurate measurement of poorly reflecting liquids, even under challenging process conditions such as
- condensate
- buildup
- foam
GWR level sensors are used in bulk solids applications for measurement of everything from cement to grain. The measuring principle is impervious to the dust rampant during filling cycles and is unaffected by extreme temperature changes.
Application examples for GWR level transmitters
Medium-sized silos for bulk solids
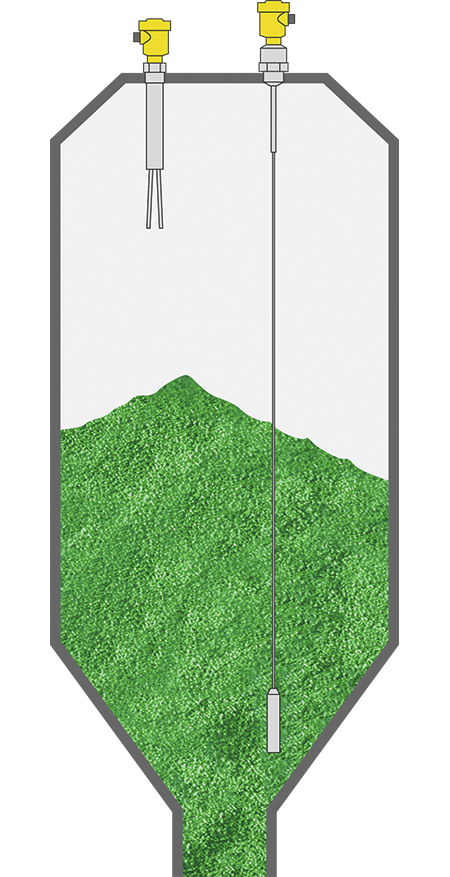
Level measurement and point level detection in silos
To the applicationOil separators
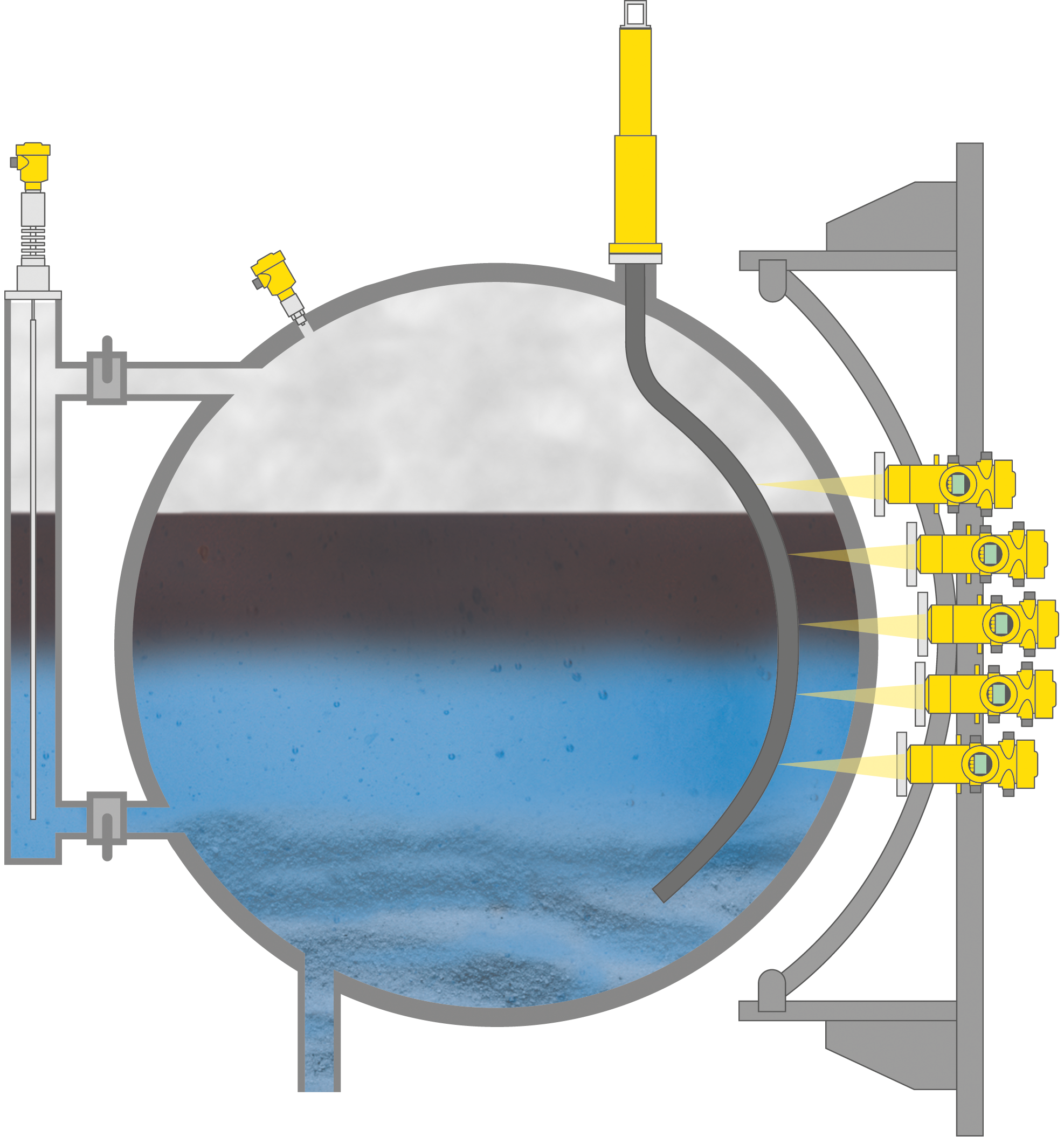
Level and pressure measurement in an oil separator
To the applicationSecondary desalter
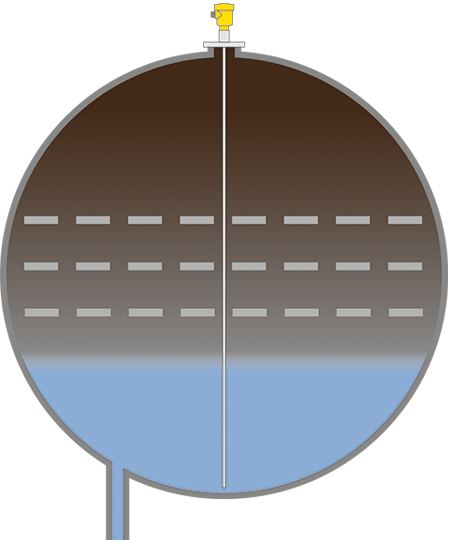
Interface measurement in the secondary desalter
To the applicationColumn trays
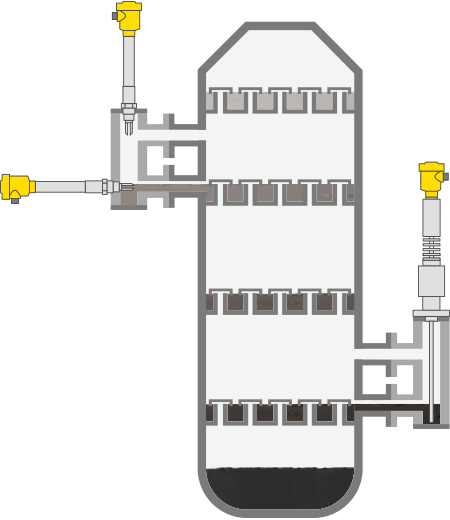
Level measurement and point level detection of column trays
To the applicationDiscover the possibilities for guided wave level measurement in your industry

Oil and gas offshore

Refining and petrochemical

Applications











Close